Definition
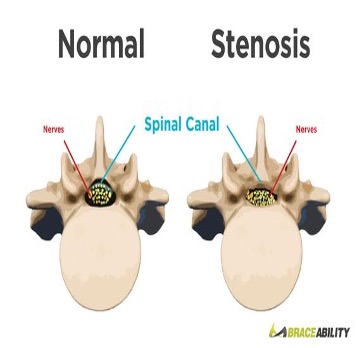
Abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. It happens when the space inside the backbone is too small.
Causes
• Wear and tear changes in the spine related to arthritis (the most common) can cause extra bone growth on the spine, cold bone spurs. They can push into the spinal canal.
• Herniated discs, of the disks soft and or material leaks out, can press on the spinal cord or nerves.
• Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy; the strong cords that help hold the bones of your spine to better can become stiff and sick over time. Thick ligaments can push into the spinal canal.
• Tumors: really, it can perform inside the spinal canal.
• Spinal injuries: trauma or motor vehicle accidents then closed spinal bones to break or move out of place. Swelling of issues after back surgery can put pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Symptoms
• Spinal stenosis often causes no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they start slowly and then get worse over time.
• Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs.
• Symptoms improve with leaning forward.
• Structural narrowing of the vertebral canal results in nerve root compression and symptomatic neurogenic claudication which do not follow a dermatomal pattern.
• Neurogenic claudication is severe pain in the lower back, buttocks and lower legs that progressively worsened by standing or walking and alleviated with forward flexion and sitting.
• Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
Diagnosis
• History, physical and neurological exam; patients typically present with symptoms of gait disturbance. They have trouble walking well after ambulating for more than a short time, neurological examination may be entirely normal at rest, but both motor and sensory loss may appear after activity.
• The hallmark of the diagnosis is sprain and weakness in both legs by walking. Typically, relieved by sitting or leaning forward.
• MRI lumbar spine: To evaluate spinal stenosis neuroforaminal stenosis, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, , nerve compression and fluids in the facets.
• Flexion extension films to evaluate stability of the spine.
Treatment: Depend on the Cause, location of the issue and severity
• Heat; better choice for osteoarthritis pain. Relax muscles, increase blood flow, and relieve achy joints.
• Cold; ice for 20 minutes can reduce swelling, tenderness and inflammation.
• Exercising; strengthening her muscles to support spine.
• Medications: NSAIDs, Gabapentin, Amitriptyline, muscle relaxants, opiates: Short term.
• Physical therapy: to gain strength and improve her balance, flexibility and spine stability.
• Pain management specialist.
• Evaluation and discussion of treatment options including:
-> Epidural steroid injections may help reduce inflammation, pain and irritation.
-> MILD procedure to remove thick ligamentum flavum that is causing compression on the spine.
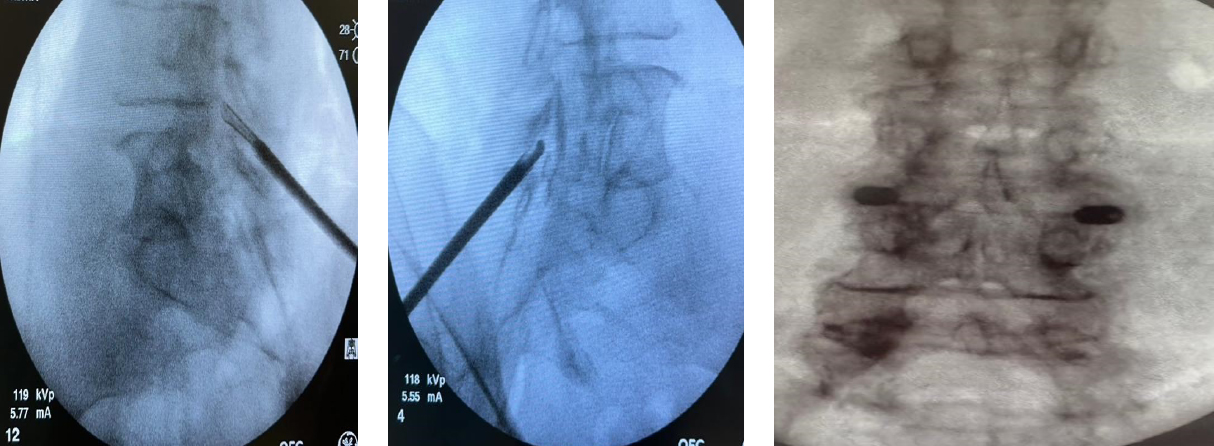
-> Interspinous Spacers: Minimally invasive surgery for some patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. We inserted spacers between the bones that extend off the back of each vertebra to keep your vertebrae apart causing more space for nerves, (Vertiflex)
-> Spinal fusion: if you have radiating nerve pain, your spine is not stable, other treatments failed. Examples: Zip-aurora, Inspan, ION (Facet Fuse)
• Neurosurgical consult for consideration of laminectomy, foraminotomy, Fusions and TLIFF or more complex cases.