Definition
Knee pain Is a common complaint that affects people of all ages.
Causes: Knee pain can be caused by injuries, mechanical problems, arthritis and others.
Injuries: ACL injury, fractures, torn meniscus, knee bursitis, patellar tendinitis.
Types of arthritis:
• Osteoarthritis; degenerative arthritis is the most common type of arthritis. It is a condition that occurs when the cartilage deteriorates with age.
• Rheumatoid arthritis; the most debilitating form of arthritis. It is an autoimmune condition that varies in severity, and it may even come and go.
• Gout: it occurs when uric acid crystals billed up in the joint. Mostly it affect big toe but it can also affect the knee.
• Pseudogout; caused by calcium containing crystals that develop in the joint fluid.
• Septic arthritis: your knee can become swollen and infected leading to swelling, pain and redness. It occurs with a fever with no history of trauma. Can quickly cause extensive damage to the knee cartilage.
Risk Factors: Excess weight, lack of muscle flexibility or strength, certain sports or occupations, and previous injury.
Symptoms:
• Swelling, stiffness, redness and warmth to touch.
• Weakness or instability.
• Popping or crunching noise.
• Inability to fully straighten the knee.
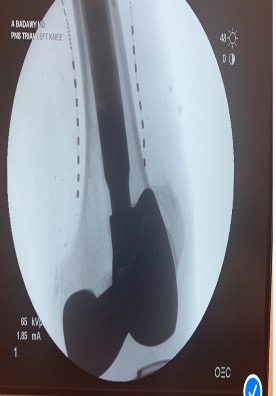
Diagnosis and Treatment:
• History and physical exam-evaluation by a specialist.
• Imaging studies: X Ray- CT scan or MRI
• Diagnostic injections, arthrogram and arthroscopy.
• Diagnostic Genicular Nerve Blocks for patients underwent total knee replacement or not candidate for surgery.
• Steroid Injections, Viscosupplementation, Prolotherapy and PRP/Stem cell injections.
• Knee supportive Braces
• RFA or Coolief Genicular Nerves, PNS or DRG Implant.
